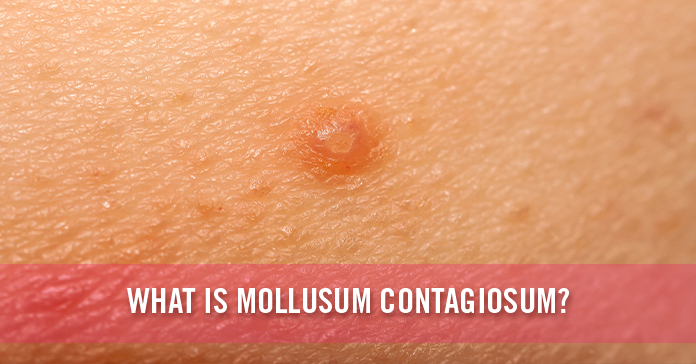
Molluscum contagiosum is a type of skin infection that is generally caused by a poxvirus. When affected the virus produces lesions or benign raised bumps on the upper part of the skin. These bumps are usually free from any sort of pain and they disappear on their own while hardly leaving any scars when left untreated. The overall timespan on which this virus lasts varies from one person to another, but these bumps can remain visible from a few months to a few years. The molluscum contagiosum disease is mostly spread by direct contact with anyone suffering from it or by touching any objects contaminated by the virus. Several types of surgical treatments and medications are available for this disease, however, in most cases, treatment isn’t necessary. Sometimes when you have a weakened immune system, treating the virus can be a bit more difficult.
Significant Symptoms Of Molluscum Contagiosum
In case anybody comes in direct contact with the virus, you might see that the overall symptoms of the infection lasting for up to six months. The average period of incubation lasts between two to seven weeks. You might also notice the appearance of small groups of painless lesions. All these bumps might appear alone or in several patchy forms. They are usually:
- White, pink, or flesh-colored.
- They might be smooth, small and shiny in appearance.
- Their central core might be filled with a sort of waxy material.
- Their diameters can be two to five millimeters.
- At times they can be shaped like a dome with a dimple or dent in the middle.
- They are usually seen in every single place of the human body except on the soles of the feet or on the palms of the hand.
In case you have a weakened immune response, you might have symptoms that are far more significant. These lesions might be as large as fifteen millimeters in diameter which is approximately the size of a dime. These bumps usually appear more often on the face and typically provides resistance from any sort of treatment.
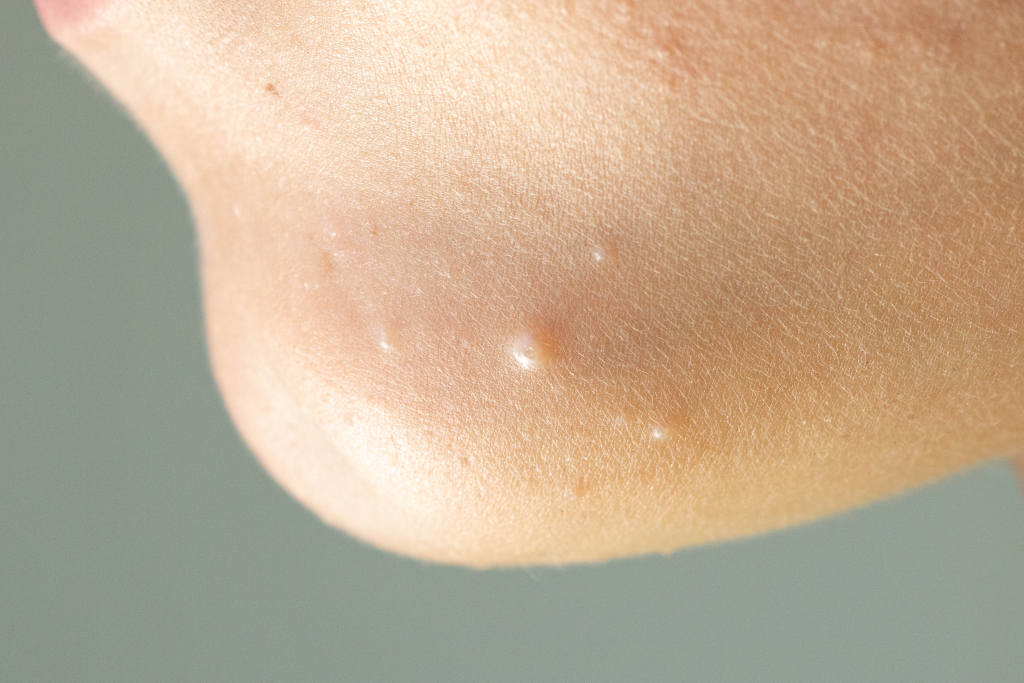
Key Risk Factors Related to Molluscum Contagiosum
Anybody and everybody might get affected by this virus, but people of certain age groups are more likely to get infected than others. The age group includes:
- People who especially stay in tropical climatic zones.
- Children between the age group of one to ten.
- People who are already suffering from atopic dermatitis, which is a very common form of eczema causing itchy rashes.
- People having weakened immune systems which are caused by factors such as cancer treatments or organ transplants.
- People who mostly participate in contact sports such as footballs or wrestling where bare skin to skin contact is most common.
How Can Molluscum Contagiosum Be Prevented?
The best way to prevent being infected by this disease is by avoiding touching the skin especially when the other person is suffering from the infection. The following suggestions might be of great help in preventing the spread of the infection.
- By practicing effective hand washing with soap and warm water.
- By avoiding touching or picking areas of the skin where bumps are present.
- Avoiding any sort of sexual contact especially if you are having bumps in the genital areas.
Remember the Molluscum Contagiosum infection is found worldwide and is most common in several developing nations. Furthermore, this disease is also traditionally regarded as a pediatric disease.